February 3, 2021
As the world looks set to add billions of smart devices in the coming years, energy efficiency is critical to enable IoT devices connected 24/7. In the past, most IoT designs have been implemented in 40nm or larger geometries, but today we see many Arm partners migrating from these mature technologies to 22nm.
Why is 22nm process a compelling option for IoT? Clearly, there is a performance advantage in moving from 40nm or even larger process nodes to 22nm, bearing in mind that raw performance is not the right scale for measuring IoT designs. Instead, the best measure is energy for a given compute task. And this is where 22nm shines.
The Rising Star: 22nm ultra-low power and ultra-low leakage
TSMC 22nm technology was developed based on its industry-leading 28nm process, a preferred foundry solution for a wide range of applications that require performance, power, and area scaling. TSMC’s 28nm process technology features high-performance and low power consumption advantages plus seamless integration with its 28nm design ecosystem to enable faster time-to-market. It enabled products to deliver higher performance, reduce energy usage, and stay eco-friendlier for years.
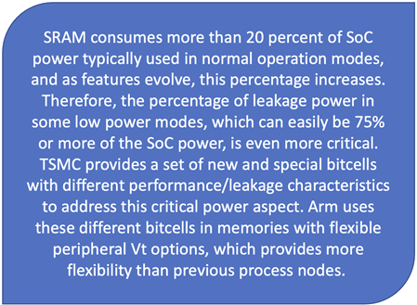 The TSMC 22nm ultra-low power (22ULP) and 22nm ultra-low leakage (22ULL) technologies were derived from the 28nm technology. Compared to 28nm high-performance compact (28HPC) technology, 22ULP technology offers significant improvements on power reduction and speed gain. These are features that are typically required by certain mobile and consumer applications, such as laptops and digital TV (DTV). The new ULL device and ULL SRAM (static random-access memory) can provide significant power reduction, which is crucial for designs in IoT and wearables.
The TSMC 22nm ultra-low power (22ULP) and 22nm ultra-low leakage (22ULL) technologies were derived from the 28nm technology. Compared to 28nm high-performance compact (28HPC) technology, 22ULP technology offers significant improvements on power reduction and speed gain. These are features that are typically required by certain mobile and consumer applications, such as laptops and digital TV (DTV). The new ULL device and ULL SRAM (static random-access memory) can provide significant power reduction, which is crucial for designs in IoT and wearables.
Depending on the product, SoC designers can choose between the performance-oriented 22ULP process or the low-power, IoT-focused 22ULL process. Arm has created 15 TSMC-sponsored SRAM/RF compilers for 22ULL and 22ULP based on 12 different bitcells from TSMC, and more are planned. Compilers for 22ULL are optimized for the low-leakage and low-power requirements, providing several power-saving features. Designers can choose between a family of performance-oriented GL and low-power ULL bitcells when designing with 22ULL. The 22ULP compilers are based on the GL bitcells.
Ambiq Designed with TSMC 22ULL and Arm IoT Solution
With an energy requirement well below 50 percent for a given compute task, TSMC 22ULL is the perfect technology for IoT applications. As a leading licensor of wireless connectivity and smart sensing technologies, Ambiq has implemented TSMC 22ULL technology and the Arm IoT solution on its newest product portfolio, Apollo4 SoC family. The Apollo4 SoC family sets new standards for ultra-low power SoC to enable intelligent endpoint IoT devices and presents the perfect combination of increased system capability with reduced power consumption for all battery-powered endpoint devices.
The Apollo4 SoC family utilizes the TSMC 22ULL process, the 32-bit Arm Cortex®-M4 core with floating-point unit (FPU), and Artisan physical IP, to achieve an unmatched low-power sleep modes executing from MRAM. It can reach up to 192MHz clock frequency with Ambiq TurboSPOT —Ambiq's ultra-low power dynamic performance scaling technology. Built on Ambiq's SPOT platform, it enables a higher frequency (HP) operating mode for the CPU and memory to run at an elevated frequency. With its accelerated 2/2.5D graphics, MIPI DSI, up to 640x480 and 32-bit color, and ultra-low power analog microphone support for always-on voice command applications, the Apollo4 SoC family is purpose-built to serve as both an application processor and a coprocessor for battery-powered endpoint devices, including smartwatches, fitness bands, remote control, predictive health and maintenance tools, and smart home appliances.
A New Level of Flexibility
TSMC 22ULL and Arm IoT offerings provide a new level of flexibility, allowing manufacturers to design a wide range of applications. But the flexibility does not stop there. Using a wide variety of logic devices for multiple periphery options, SoC designers can now use the TSMC 22nm process for performance-oriented designs in the GHz range or ultra-low power <100MHz designs. The diagram below shows the power-performance range of compilers using the high-density bitcell, for 22ULP with GL bitcell, 22ULL with GL bitcell, and 22ULL with ULL bitcell. Each of these three compilers also has three periphery options.
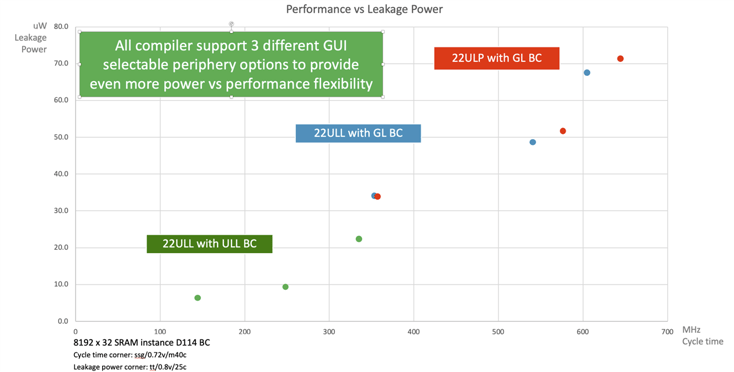
This TSMC 22nm process flexibility combined with Arm Artisan physical IP enable a wide range of IoT applications, such as the low-power Ambiq Apollo4 SoC with Cortex-M4. Designs utilizing newer Arm cores, such as Cortex-M55 and Ethos-U55, can achieve even greater benefit in demanding endpoint-AI applications.
There are currently more than 100 customers actively using Arm physical IP on a TSMC 22nm process. The goal of Arm is to help partners succeed.