July 3, 2024

Figure 1, Industry 4.0
The fourth Industrial revolution, or “Industry 4.0” is transforming every aspect of the way goods are made. Industrial automation processes are becoming smarter and more integrated, leading to the creation of “flexible factories” and also revolutionising the logistic processes associated with manufacture and delivery. This is changing companies globally, the products we can buy, the jobs we do, and the productivity of the entire manufacturing and supply chain.
A large number of enabling technologies are involved, all of which are competing to deliver the absolute maximum disruption. By replacing manual or semi-automated processes with fully connected and smart automation, Industry 4.0 is also delivering much greater flexibility. This is improving levels of business responsiveness and facilitating greater levels of product customization whilst also augmenting yield and efficiency.
In order to fully understand the impact of industry 4.0 is it useful to briefly discuss the context of the evolutions that preceded it and therefore made it possible.
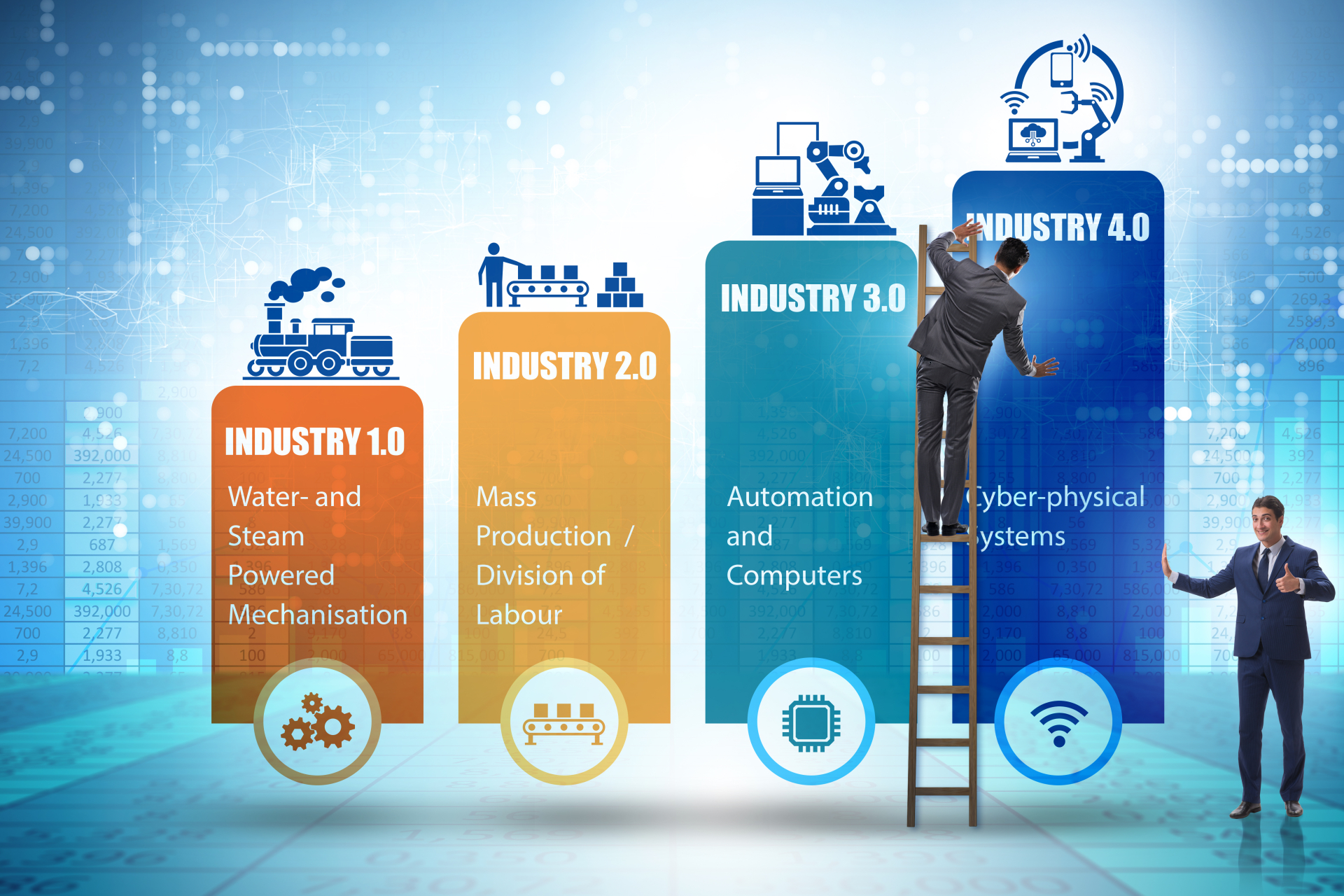
Figure 2, Industrial revolutions

Figure 3, Industry 4.0 is the large-scale system integration of a huge number of different technologies
The mother of the “Big Data” associated with Industry 4.0 is the myriad of sensor technologies that supply the raw data. The number of parameters sensors can measure has increased dramatically, and combined with strong market growth, these devices are now highly accessible. In many cases the interfaces to these sensors are either simple analogue or digital, interfaces including serial, I2C, SPI, RS232 and RS485 current loop.
TOP-electronics distributes W&T, which is a German brand of Industrial Automation devices including sensor interfaces offering multiple analogue or digital inputs. They also have a huge range of sensor products and modules. (Click the blue links to view these products).
Automation and Robotics are at the forefront of Industry 4.0. From a practical standpoint these technologies often perform the process or physical tasks required to produce goods from components or raw materials.

Figure 4, Much of the Big Data comes from Sensors
These processes are becoming more connected, integrated, programmable and flexible, allowing for many more varied, customized products to be created on a single production line, creating so-called “flexible factories”.
W&T has an extensive product range of industrial automation products. TOP-electronics also has a complete portfolio of motion control products for robotics.

Figure 5, The Internet of Things
The internet of things is all about connecting smart sensors, devices and machines to networks of all kinds to share information, interact and do clever things. The “smart” aspect of these devices means they have on board processing which may also include other technologies such as A.I. machine learning or traditional software.
Within industrial environments, this also involves connecting machines and sensors on production lines to enable greater flexibility, integration, responsiveness and insight into processes.
The main standard for IoT messaging over the internet is called MQTT which is a client-server protocol based on TCP/IP. It defines how IoT devices can publish and subscribe to data. These interactions always take place through a device called a MQTT broker which allows the devices to communicate through topics and to be decoupled from each other. Top offers a range of MQTT Broker products.
IoT products encompass all domains in terms of connectivity options. In addition to Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, another example of an open wireless standard for IoT communications is LoRa. This is a long range, very low power radio technology, that with an outdoor gateway, allows up to 2-3km of communication range in urban environments, and up to 7km in rural areas. Top distributes a portfolio of LoRa modules, gateways and antenna products. Another important wireless standard for industrial use cases is Zigbee and Top also carries Zigbee compliant products and antennas.
Implicit within sharing IoT data is the paramount requirement to ensure that systems and data stays completely secure. W&T manufactures a range of industrial firewall products that are used to help ensure the secure operation of all connected devices.
5G is another key enabling technology for industry 4.0. When fully deployed, 5G will facilitate 1/10th of the latency when compared with 4G, ten times greater bandwidth, and ten times the number of connected devices per infrastructure node. These aspects help facilitate the backbone necessary for many new and existing use cases involved in Industry 4.0.
The very low latency can be especially useful in industrial applications, and the multitude of use-cases includes synchronisation of machines and other equipment.
Top offers 5G modules from Quectel and antenna solutions from Summit and 2J as well as several other vendors.
Wi-Fi also has an important role as an enabling technology for Industry 4.0 because many use cases involve collecting IoT and other data and communicating with devices that already use these standards.
Built into Wi-Fi 6 are many new Quality of Service (QoS) features such as the traffic prioritization and Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) to provide more deterministic performance. The associated IEEE standards for the Mac and Physical layers used for Wi-Fi now also include Fine Timing Measurement (FTM) which allows Wi-Fi to also be used for synchronisation.
TOP-electronics distributes LM Technologies which make Wi-Fi modules and dongles. They also distribute Silex which makes Wi-Fi to Serial and Ethernet products for rapid integration in industrial environments.
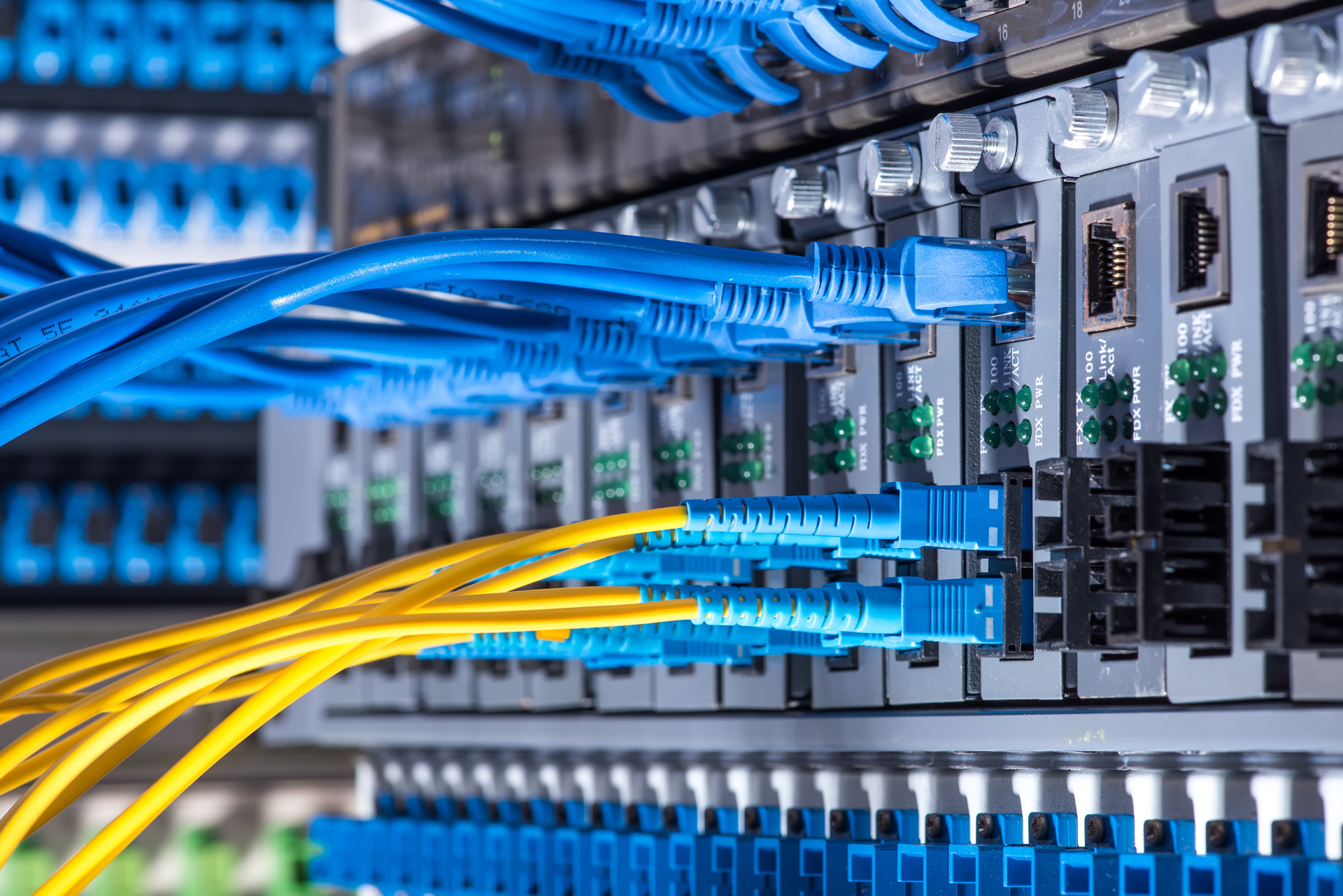

Figure 6, Fiber Optics
Fiber is a vital technology for Industry 4.0 because it is immune to electrically radiated and induced noise that can disrupt both wired and wireless networks. This type of noise can be present in certain industrial environments, often due to the operation of large power machines. Fiber permits noise-resistant networks to be constructed in industrial locations and also allows extremely long connectivity distances to be spanned without the need for repeaters. This also enables ultra-fast low latency communication and file sharing between district business operations or locations.
Top and W&T have a large range of fiber products for plastic optical fibre as well as singlemode and multimode glass fiber optics.
The widespread availability of low-cost, high-resolution visible light and thermal cameras is helping drive industry 4.0 by enabling automation of various industrial processes such as part handling and tracking, as well as process and quality control.
 |
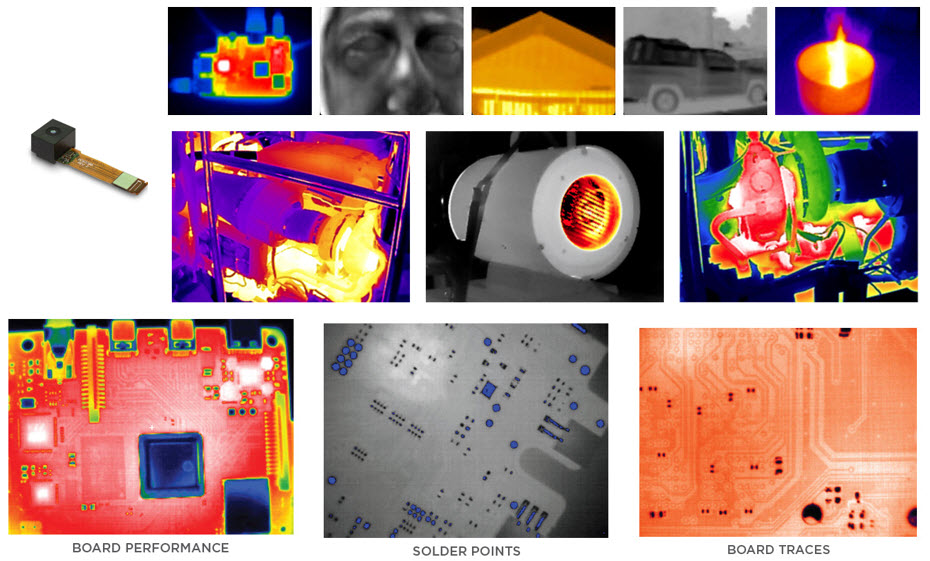 |
Figures 7, Use of Thermal Cameras with AI
The processing for these use-cases is shifting from regular computing resources towards AI because the latter can process images more readily and the training process is often simpler than programming other forms of image recognition software. One use case example for access control is the use of thermal cameras in certain public areas to help determine people that may be carrying COVID. Top Electronics carries the Seek Thermal Range of Thermal cameras.
Edge and Cloud computing both have distinct and vital roles to play in Industry 4.0.
Edge processing differs from Cloud computing, because the computational resources are placed on the edge of the required network rather than in the cloud. Being placed on the edge, they are physically close to other devices on the network which means that the compute tasks can be completed more rapidly with minimal latency.
Edge Computing can also be used to offload other processing overhead from other connected network devices, for example using Edge Processing power to offload the required processing inside smart devices and sensors connecting or reporting data. This also reduces the power requirements inside these devices or sensors.
A popular example is voice recognition deployed inside numerous smart loudspeaker consumer products, which uses edge computational resources to reduce latency.
Cloud computing is also vital to Industry 4.0 because it enables cost-effective, large-scale data integration of different business services, units and sites for centralised processing and analysis. For example, to integrate the business operations of engineering, production, supply chain, sales and distribution, and after sales service. The power of Cloud and Edge services can be combined in many ways to leverage the strengths of both approaches, for example to provide rapid website hosting worldwide using a Content Delivery Network (CDN). This uses local servers in each country to supply content rapidly. A central server redirects the incoming visitors to a network of edge servers in each country. These are selected dependent on the visitor location and detected on the incoming IP address so that webpages load quickly in every country.
There are many other similar architectures designed to allow both low-latency local processing combined with the larger scales provided by cloud services. The smart loudspeaker example mentioned earlier also uses cloud services as well as edge severs and AI…
Which brings neatly onto the subject of AI J…
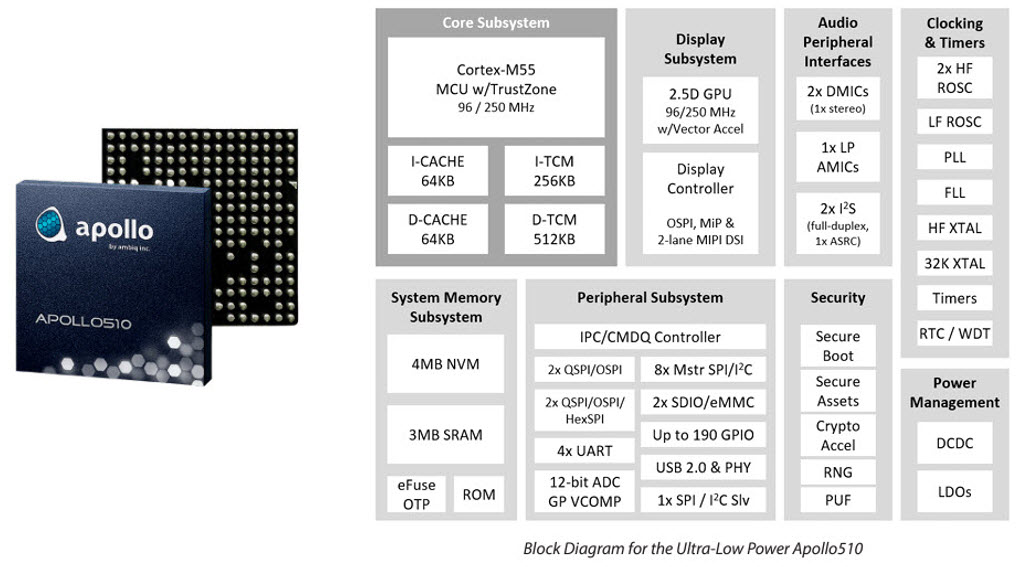
Figure 8, Ambiq is at the forefront of the AI internet of things, source Ambiq
AI, artificial intelligence also referred to as machine learning, allows companies to leverage the power of data and big data, by being able to spot relationships within the incoming data. This applies to all areas of business, and is not limited to production. These relationships can provide better insights into which processes need to be tweaked and updated. Sub-Threshold Edge computing combined with intelligent IoT and AI-of-Things is enabling a new era of ultra-smart devices to be deployed that have battery life times that can be measured in years.
One production-related example is in the area of predictive maintenance. This is where multiple incoming sensor data is used to predict when maintenance cycles are due just before they are required. Ambiq is a pioneering supplier working in the area of intelligent endpoints and the AI-of-Things.
The transformative process of Industry 4.0 has allowed organisations to create so called “digital twins” of processes, production lines, factories and logistic processes. These digital twins are replicas of the physical world represented in digital form. They are created by pulling real data from sensors machines and processes and providing a modelled simulation. These digital twins allow for changes to be evaluated and optimised prior to implementation, and for expected outcomes and results to be better understood. It also allows a better understanding of how new products can be engineered to be better optimised ready for a given production process.
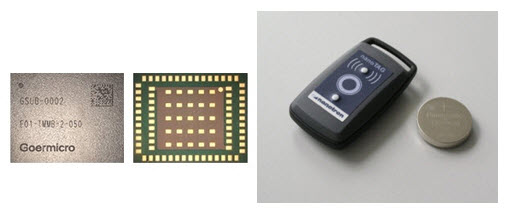

Figure 9, Real Time Location Solutions from Goermicro, Inpixon and Elatec
The widespread use of Barcode, RF I.D. and Real Time Location Systems are also all critical ingredients for industry 4.0, because these technologies allow assets to be tracked and located. RTLS is particularly useful in combination with other industry 4.0 enabling technologies such as mobile robotics to provide exact tracking of a devices location.
TOP carries a large range of RFiD and RTLS products.
The fourth industrial revolution is fully underway with many different disruptive technologies involved and competing for space. Industry 4.0 is significantly different to its predecessors because there are so many more different technologies involved. This document discusses a sub-section of some of the prominent contributing technologies but is by no way a complete list. From a system level, the huge number of technologies also means there is larger diversity in the way these technologies can be integrated together to transform manufacturing and logistics processes. Sensors, automation, robotics, big data, edge and cloud services, IoT, high-speed low-latency communication technologies, A.I., digital twins, location and identification all play their own pivotal roles in facilitating and enabling the transformation.

Figure 10, People are our best Resource
At the centre of every companies’ success of failure in the fourth industrial revolution is a complex System Integration process with a huge number of competing options regarding how each problem can be solved. These decisions to select the correct technology for each process are extremely complex in nature and have to be made by knowledgeable individuals with an understanding of all the options. People therefore are our best resource for helping enable the current industrial revolution. Having knowledgeable people, to make informed choices about the integration of technology options is the key to success with Industry 4.0
If you have any questions about how you can tackle an Industry 4.0 challenge or accelerate your integration, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us today.
Please contact [email protected]